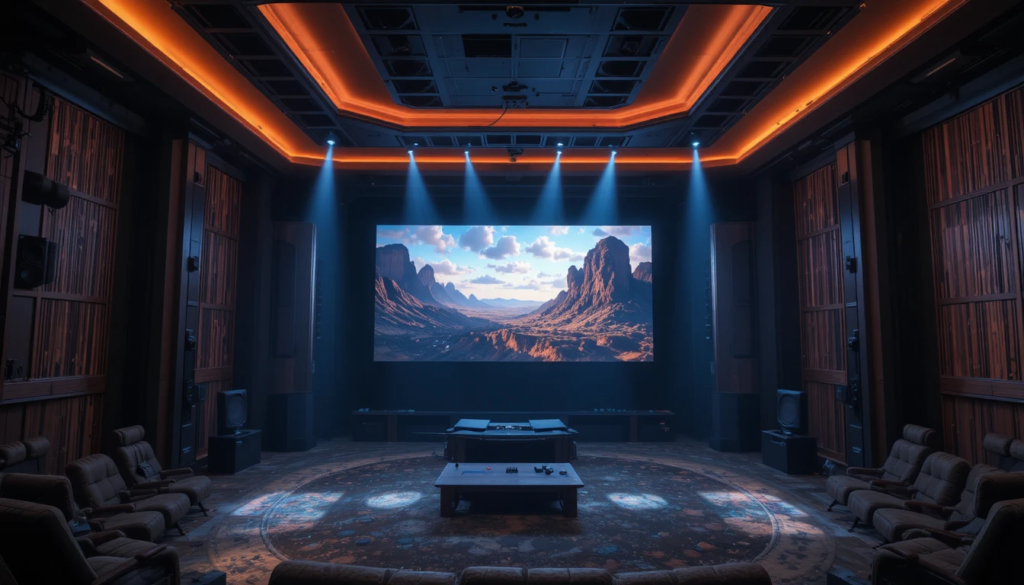
What Is Dolby Atmos?
Dolby Atmos is an advanced surround-sound technology developed by Dolby Laboratories to create a three-dimensional, highly immersive audio environment that moves sound around a listener with exceptional realism. Unlike traditional surround-sound formats that rely on channels—such as 5.1 or 7.1 systems—Dolby Atmos uses object-based audio, a method that treats each sound as an independent “object” that can be precisely placed and moved in 3D space. This approach enables sound to be projected not only around the audience but also above them, effectively adding a vertical dimension to audio reproduction. The result is a soundscape that mimics natural hearing, enveloping the listener in a dome of sound that responds dynamically to the on-screen action.


How Dolby Atmos Differs from Traditional Surround Sound
Traditional surround-sound systems distribute audio across a predetermined number of channels. For example, 5.1 surround uses five speakers arranged around the room and one subwoofer for low-frequency effects. Each sound effect or musical component is mixed into a specific channel, which limits the system’s ability to provide precise localization or movement. Dolby Atmos, however, is not restricted by channels. Instead, audio engineers can place up to 128 individual sound objects anywhere within a 360-degree space. The playback system interprets these object positions and adapts them to the speaker layout available in the listener’s environment. This means the same Dolby Atmos mix can deliver a rich, accurate experience whether it is played in a full theatrical setup with dozens of speakers or a compact home system with only a handful of speakers. The flexibility and scalability of Atmos make it fundamentally different from legacy surround formats.
The Concept of Audio Objects in Dolby Atmos
The heart of Dolby Atmos lies in the idea of audio objects. In traditional mixes, sounds are grouped together and routed to specific channels. In an Atmos mix, each sound object can exist independently, carrying its own metadata that defines where it should be placed and how it should move through three-dimensional space. This allows for incredibly detailed sound design. Footsteps can approach from behind, leaves can rustle overhead, or raindrops can fall from above in a way that feels lifelike and unrestricted by speaker positions. The object-based paradigm grants sound designers creative freedom to build expansive, intricate audio worlds.
The Speaker Configuration and Height Channels
One of the most recognizable features of Dolby Atmos is the addition of height channels. While a full theatrical Atmos setup can include dozens of speakers strategically placed throughout the venue, home Atmos systems commonly use configurations like 5.1.2, 5.1.4, 7.1.2, or 7.1.4. The last digit represents the number of height speakers. Even soundbars now incorporate upward-firing drivers to recreate the height effects in rooms where installing ceiling speakers is not practical. These configurations provide a scalable path for different environments while preserving much of Atmos’s spatial fidelity.
Dolby Atmos in Cinemas
Dolby Atmos was first introduced to the public in commercial cinemas, where its impact was immediately noticeable. Movie theaters equipped with Atmos use a large number of speakers positioned around the auditorium, including overhead arrays that enable a full 3D sound dome. This setup allows sound designers to place audio objects anywhere in the space with remarkable accuracy. Action scenes gain depth, tension increases as sound moves fluidly, and quiet moments feel more intimate due to Atmos’s ability to isolate subtle details. Theatrical Atmos also supports a wide dynamic range and clarity, which enhances the emotional impact of films. For audiences, the result is a cinematic experience where the boundaries between screen and auditorium blur, pulling them deeper into the story.
Dolby Atmos for Home Theaters
As home theater technology became more accessible, Dolby Atmos quickly expanded into the consumer market. Home theater receivers and speaker systems began incorporating Atmos compatibility, enabling enthusiasts to experience cinematic audio at home. A typical home Atmos setup includes height speakers added to traditional surround configurations, but even without a complex installation, many people can enjoy Atmos through soundbars and compact speaker systems. These devices use processing algorithms and carefully angled drivers to simulate the overhead sound effect in smaller spaces. With streaming platforms offering Atmos-encoded content, it has become easier for home viewers to enjoy immersive sound without specialized equipment. Whether through a full home theater system or a single soundbar, Atmos enhances movies, games, and television with depth and dimension previously limited to theaters.
Dolby Atmos in Streaming and Digital Media
The growth of streaming services has played a major role in the widespread adoption of Dolby Atmos. Platforms such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, Apple TV+, and many others now support Atmos playback for a wide range of movies, series, and documentaries. This allows viewers to enjoy immersive audio without physical media. The combination of high-quality video formats like 4K HDR and Atmos further elevates home entertainment by delivering both visual and auditory immersion. Additionally, digital distribution enables content creators to experiment with Atmos mixes for independent films, online videos, and experimental media. As broadband speeds improve globally, streaming Atmos content becomes increasingly accessible, pushing immersive audio into mainstream entertainment.
Dolby Atmos in Music and Audio Production
One of the most exciting recent developments is the introduction of Dolby Atmos to music production. Traditionally, music mixes have been stereo, with occasional multi-channel releases. Atmos changes the approach entirely by allowing songs to be mixed in 3D space. Musicians and producers can position vocals, instruments, and effects around the listener. Streaming services like Apple Music, Tidal, and Amazon Music offer Spatial Audio or 3D Audio experiences powered by Atmos. This has opened new creative possibilities, encouraging artists to experiment with immersive arrangements that go beyond the limitations of stereo. The result is a more engaging and emotionally resonant listening experience.
Dolby Atmos in Gaming
Gaming is another domain where Dolby Atmos has made significant impact. Modern video games aim to create believable worlds, and immersive audio is essential for achieving realism. Atmos allows game developers to position sounds accurately—enemies approaching from above, environmental cues surrounding the player, or dramatic effects that heighten tension. For competitive gaming, Atmos can improve situational awareness by enabling players to locate sounds precisely. This positional accuracy is especially valuable in first-person shooters or adventure games where directional audio influences gameplay decisions. Many gaming consoles and PCs now support Atmos, making it accessible to a large audience of players who want deeper immersion and strategic advantage.
Dolby Atmos and Headphones
Atmos for headphones uses binaural rendering to simulate 3D sound through just two drivers. The technology processes audio objects and applies head-related transfer functions (HRTFs) to mimic how sound interacts with the human ear from various directions. The result is a surprisingly accurate sense of space and direction that does not require special hardware beyond a standard pair of headphones. This feature is widely available on smartphones, streaming apps, gaming devices, and PCs. With software processing, headphone-based Atmos brings immersive audio to users who may not have space or budget for full surround systems.
Dolby Atmos in Soundbars and Compact Systems
For many people, full speaker installations are impractical due to limited space or aesthetic preferences. Dolby Atmos soundbars provide an elegant solution by integrating multiple drivers—including upward-firing units—into a single compact device. These soundbars use acoustic reflection to bounce audio off the ceiling, creating the illusion of overhead sound. Advanced models combine this with room-correction technology to adapt sound to the room’s acoustics. While not as precise as dedicated ceiling speakers, Atmos soundbars can deliver an impressively immersive experience with minimal setup. This accessibility has accelerated the adoption of Atmos in homes worldwide, making immersive sound easy to achieve.
Impact of Dolby Atmos on Content Creation
For filmmakers, musicians, and developers, Dolby Atmos offers a powerful toolkit for crafting immersive experiences. The technology encourages creative sound design by freeing artists from channel constraints. Film soundtracks gain depth, music mixes offer new expressive potential, and game worlds become more lifelike. Production studios increasingly support Atmos mixing rooms, and software tools like Pro Tools, Logic Pro, Nuendo, and Dolby’s own Atmos Renderer have become standard in modern audio workflows. As more creators adopt object-based sound design, audiences benefit from richer, more dynamic content across media formats.
Future of Dolby Atmos and Immersive Audio
Dolby Atmos continues to evolve as immersive audio becomes a defining feature of modern entertainment. Emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) rely heavily on spatial audio to create believable experiences. Atmos fits naturally into this trend by providing detailed positioning and movement of sound objects. As VR headsets and AR devices advance, spatially accurate sound will play a crucial role in user immersion. Furthermore, advancements in AI-driven audio processing and personalized HRTFs may enhance headphone-based Atmos, offering even more realistic spatial cues tailored to individual listeners. The future promises broader adoption and deeper integration of immersive audio in everyday media consumption.
Conclusion
By moving beyond traditional channels and embracing object-based design, Atmos creates a three-dimensional soundstage that surrounds the listener from every direction—even above. Its versatility allows it to scale from large cinemas to compact home soundbars and standard headphones, making immersive audio accessible to nearly everyone. Whether in movies, music, games, or virtual environments, Dolby Atmos enhances storytelling, increases realism, and elevates emotional impact. As immersive audio becomes more integral to modern entertainment, Dolby Atmos stands at the forefront, shaping the future of how we hear the world around us.